728x90
반응형
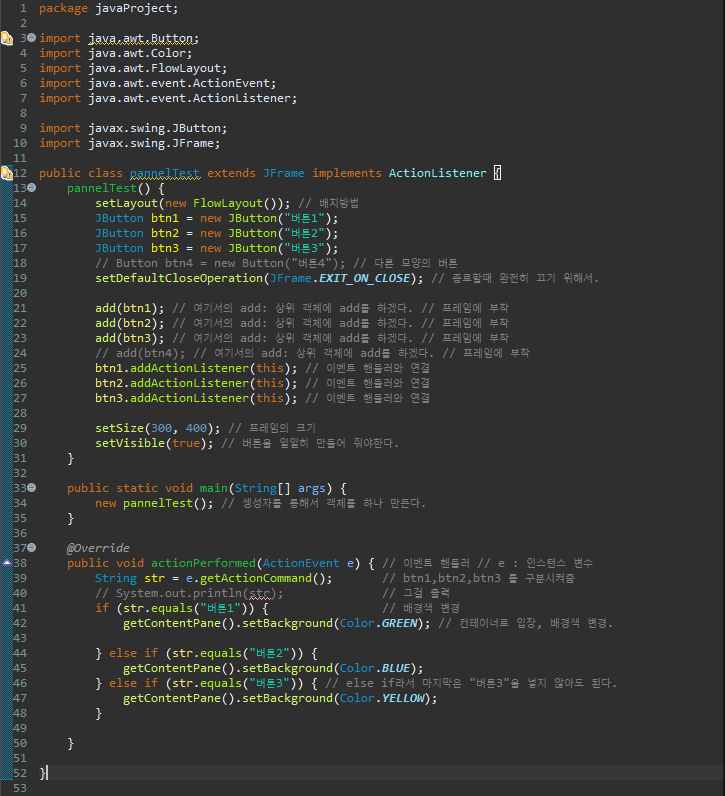
package javaProject;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class pannelTest extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
pannelTest() {
setLayout(new FlowLayout()); // 배치방법
JButton btn1 = new JButton("버튼1");
JButton btn2 = new JButton("버튼2");
JButton btn3 = new JButton("버튼3");
// Button btn4 = new Button("버튼4"); // 다른 모양의 버튼
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 종료할때 완전히 끄기 위해서.
add(btn1); // 여기서의 add: 상위 객체에 add를 하겠다. // 프레임에 부착
add(btn2); // 여기서의 add: 상위 객체에 add를 하겠다. // 프레임에 부착
add(btn3); // 여기서의 add: 상위 객체에 add를 하겠다. // 프레임에 부착
// add(btn4); // 여기서의 add: 상위 객체에 add를 하겠다. // 프레임에 부착
btn1.addActionListener(this); // 이벤트 핸들러와 연결
btn2.addActionListener(this); // 이벤트 핸들러와 연결
btn3.addActionListener(this); // 이벤트 핸들러와 연결
setSize(300, 400); // 프레임의 크기
setVisible(true); // 버튼을 일일히 만들어 줘야한다.
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new pannelTest(); // 셍성자를 통해서 객체를 하나 만든다.
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // 이벤트 핸들러 // e : 인스턴스 변수
String str = e.getActionCommand(); // btn1,btn2,btn3 를 구분시켜줌
// System.out.println(str); // 그걸 출력
if (str.equals("버튼1")) { // 배경색 변경
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.GREEN); // 컨테이너로 입장, 배경색 변경.
} else if (str.equals("버튼2")) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.BLUE);
} else if (str.equals("버튼3")) { // else if라서 마지막은 "버튼3"을 넣지 않아도 된다.
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
}
}
}
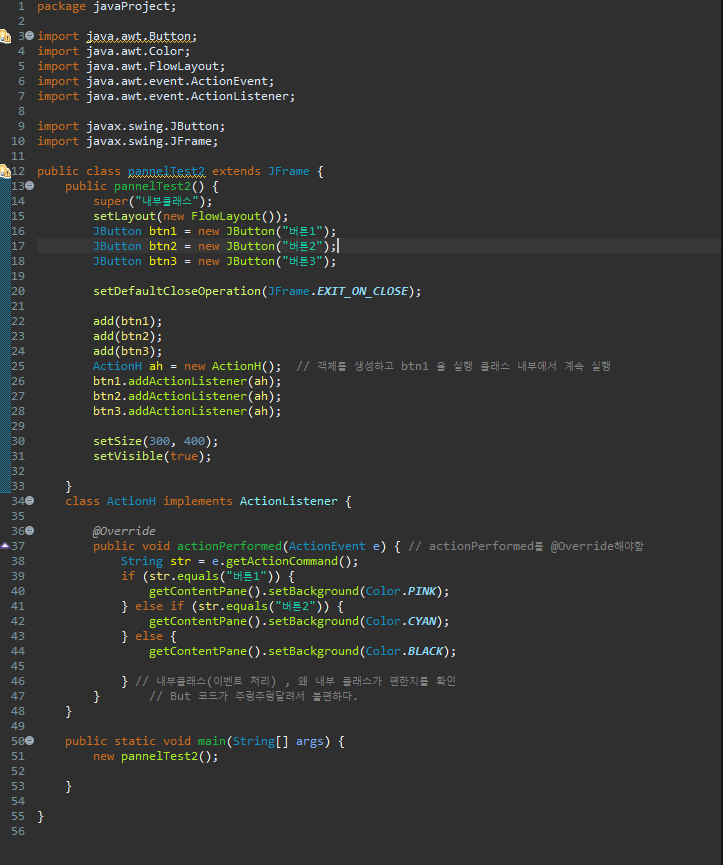
package javaProject;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class pannelTest2 extends JFrame {
public pannelTest2() {
super("내부클래스");
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn1 = new JButton("버튼1");
JButton btn2 = new JButton("버튼2");
JButton btn3 = new JButton("버튼3");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(btn1);
add(btn2);
add(btn3);
ActionH ah = new ActionH(); // 객체를 생성하고 btn1 을 실행 클래스 내부에서 계속 실행
btn1.addActionListener(ah);
btn2.addActionListener(ah);
btn3.addActionListener(ah);
setSize(300, 400);
setVisible(true);
}
class ActionH implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // actionPerformed를 @Override해야함
String str = e.getActionCommand();
if (str.equals("버튼1")) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.PINK);
} else if (str.equals("버튼2")) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.CYAN);
} else {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.BLACK);
} // 내부클래스(이벤트 처리) , 왜 내부 클래스가 편한지를 확인
} // But 코드가 주렁주렁달려서 불편하다.
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new pannelTest2();
}
}
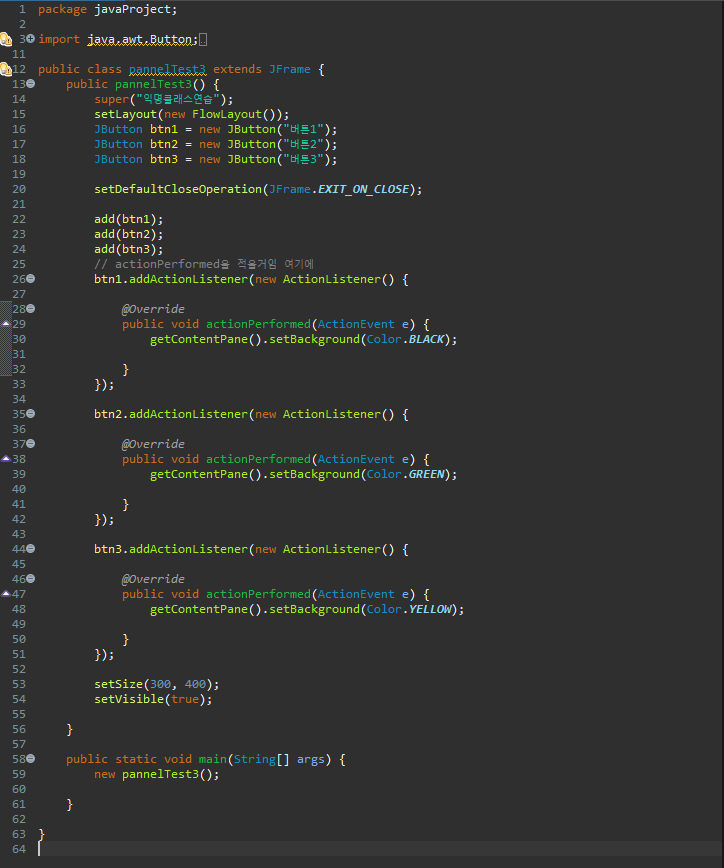
package javaProject;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class pannelTest3 extends JFrame {
public pannelTest3() {
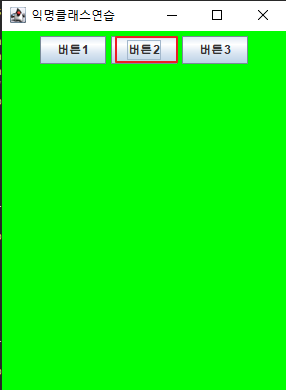
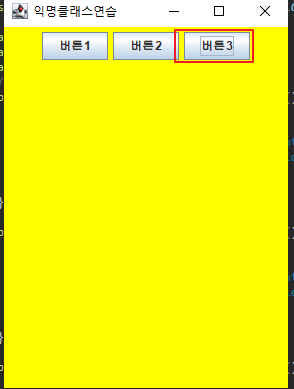
super("익명클래스연습");
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn1 = new JButton("버튼1");
JButton btn2 = new JButton("버튼2");
JButton btn3 = new JButton("버튼3");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(btn1);
add(btn2);
add(btn3);
// actionPerformed을 적을거임 여기에
btn1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.BLACK);
}
});
btn2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.GREEN);
}
});
btn3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
}
});
setSize(300, 400);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new pannelTest3();
}
}

728x90
반응형