728x90
반응형


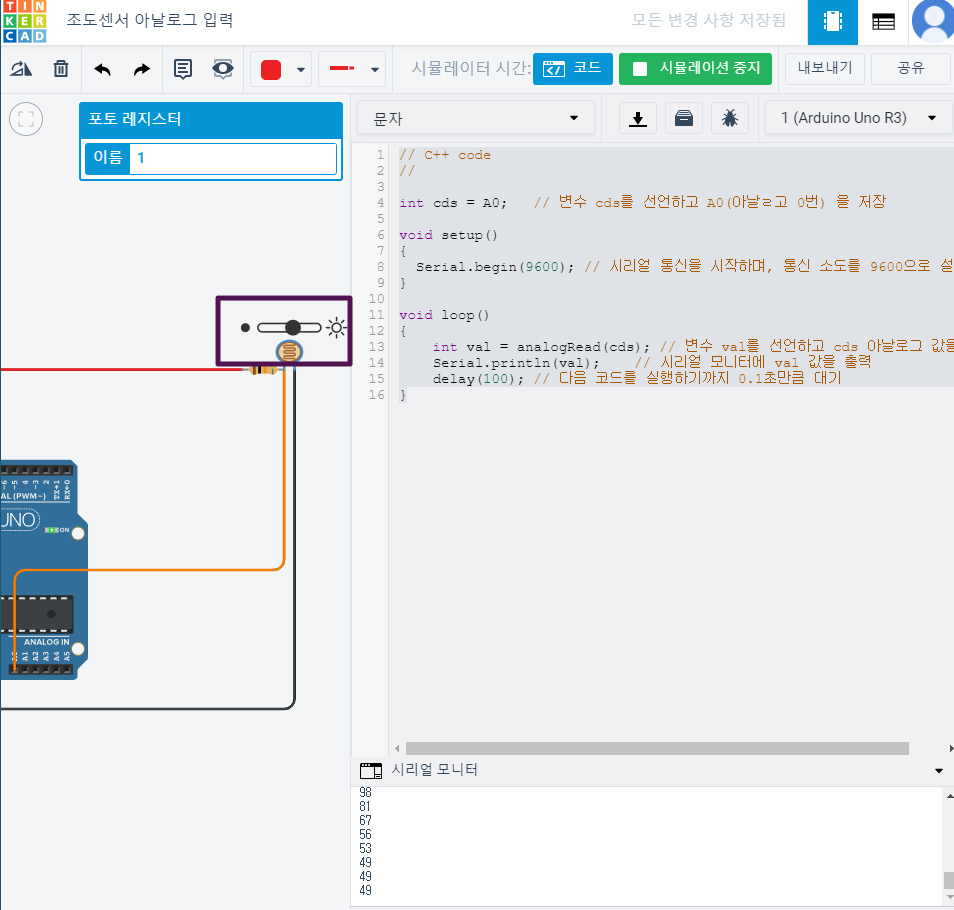
// C++ code
//
int cds = A0; // 변수 cds를 선언하고 A0(아날ㄹ고 0번) 을 저장
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // 시리얼 통신을 시작하며, 통신 소도를 9600으로 설정
}
void loop()
{
int val = analogRead(cds); // 변수 val를 선언하고 cds 아날로그 값을 저장
Serial.println(val); // 시리얼 모니터에 val 값을 출력
delay(100); // 다음 코드를 실행하기까지 0.1초만큼 대기
}가변저항 아날로그 입력


// C++ code
//
int val = 0; // 변수 val를 선언하고 0으로 초기화
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // 시리얼 통신을 시작한다 .속도는 9600
}
void loop()
{
val = analogRead(A0); // 변수 val에 A0핀의 아날로그 입력 값 대입
Serial.println(val); // 시리얼 모니터에 val 값 출력
delay(100); // 0.1 초 딜레ㅣㅇ
}- LED 밝기 조절하기 (아날로그 신호 출력)
PWM은 Pulse Width Modulation의 약자, 진동의 폭을 조절한다는 의미


// C++ code
//
void setup()
{
pinMode(6, OUTPUT); // 6번 핀을 출력모드로 설정
}
void loop()
{
for (int i = 10; i < 255; i = i+10) {
analogWrite(6,i); // LED (6번 핀)에 i 만큼의 아날로그 신호 출력
delay(100); // 0.1초 딜레이
}
}

/*
멜로디 톤 아래의 C4==음, 숫자 == 주파수
#define은 앞의 변수값을 뒤의 값으로 선언한다.*ex) NOTE_C4 = 262로 선언
*/
#define NOTE_C4 262
#define NOTE_G3 196
#define NOTE_A3 220
#define NOTE_B3 247
#define NOTE_C4 262
// notes in the melody:
// 멜로디 배열 선언 5개의 음의 주파수를 입력
int melody[] = {
NOTE_C4, NOTE_G3, NOTE_G3, NOTE_A3, NOTE_G3, 0, NOTE_B3, NOTE_C4
};
// note durations: 4 = quarter note, 8 = eighth note, etc.:
// 음의 길이 : 4 = 1/4박자, 8 = 1/8박자
int noteDurations[] = {
4, 8, 8, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4
};
void setup() {
// iterate over the notes of the melody:
// 한번만 실행
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < 8; thisNote++) {
// to calculate the note duration, take one second
// divided by the note type.
//e.g. quarter note = 1000 / 4, eighth note = 1000/8, etc.
// 1/4 박자 = 1000 / 4, 1/8 박자 = 1000 / 8
int noteDuration = 1000 / noteDurations[thisNote];
// tone(핀번호, 음주파수, 시간)
tone(8, melody[thisNote], noteDuration);
// to distinguish the notes, set a minimum time between them.
// the note's duration + 30% seems to work well:
// 음과 음 사이의 대기시간
int pauseBetweenNotes = noteDuration * 1.30;
delay(pauseBetweenNotes);
// stop the tone playing:
noTone(8);
}
}
void loop() {
// no need to repeat the melody.
}LCD


/*
LiquidCrystal Library - Hello World
Demonstrates the use a 16x2 LCD display. The LiquidCrystal
library works with all LCD displays that are compatible with the
Hitachi HD44780 driver. There are many of them out there, and you
can usually tell them by the 16-pin interface.
This sketch prints "Hello World!" to the LCD
and shows the time.
회로
The circuit:
* LCD RS pin to digital pin 12 :: LCD의 RS핀과 아두이노 12번 핀을 연결
* LCD Enable pin to digital pin 11
* LCD D4 pin to digital pin 5
* LCD D5 pin to digital pin 4
* LCD D6 pin to digital pin 3
* LCD D7 pin to digital pin 2
* LCD R/W pin to ground
* LCD VSS pin to ground
* LCD VCC pin to 5V
* 10K resistor: 가변저항 : 밝기 조절
* ends to +5V and ground
* wiper to LCD VO pin (pin 3) 가변저항 가운데 조절
Library originally added 18 Apr 2008
by David A. Mellis
library modified 5 Jul 2009
by Limor Fried (http://www.ladyada.net)
example added 9 Jul 2009
by Tom Igoe
modified 22 Nov 2010
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/LiquidCrystal
*/
// LCD 라이브러리를 불러온다
// include the library code:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
// LCD 를 초기화 한다. (이때 핀 번호가 맞는지 확인한다.)
// initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
void setup() { // 한번만 실행
// LCD 시작(16x2) 16열 2행
// set up the LCD's number of columns and rows:
lcd.begin(16, 2);
// LCD에 글자 출력(첫번째 줄)
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.print("hello, world!");
}
void loop() { // 메인을 계속 실행
// 커서의 위치(index)를 0,1 ( 0이 가로 위치, 1이 세로 줄 위치)
// set the cursor to column 0, line 1
// (note: line 1 is the second row, since counting begins with 0):
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// 1000ms => 1초, LCD 켜진 이후 ms/1000 초로 출력 :
// print the number of seconds since reset:
lcd.print(millis() / 1000);
}
초음파 거리센서
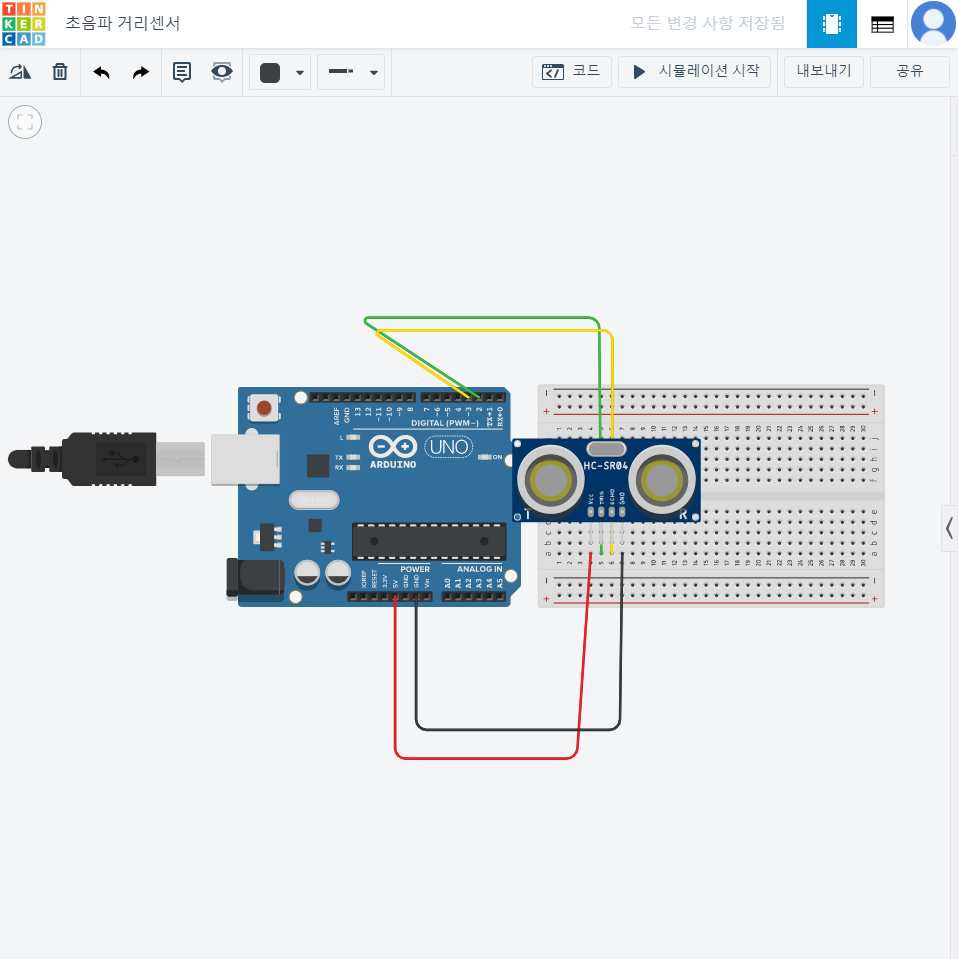

// C++ code
//
int trig = 2;
int echo = 3;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(trig,OUTPUT);
pinMode(echo,INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// trig핀으로 초음파 측정 시작
digitalWrite(trig,HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10); // 10us 마이크로세컨드
digitalWrite(trig,LOW);
// 에코핀에 입력이 high까지 걸리는 시간(초음파 되돌아 올때까지의 시간)
// 되돌아온 시간 * 340미터/2 (센티미터로 변환)
int distance = pulseIn(echo,HIGH) * 17 /1000;
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println("cm");
delay(100); // 딜레이 0.1
}서보모터 사용하기
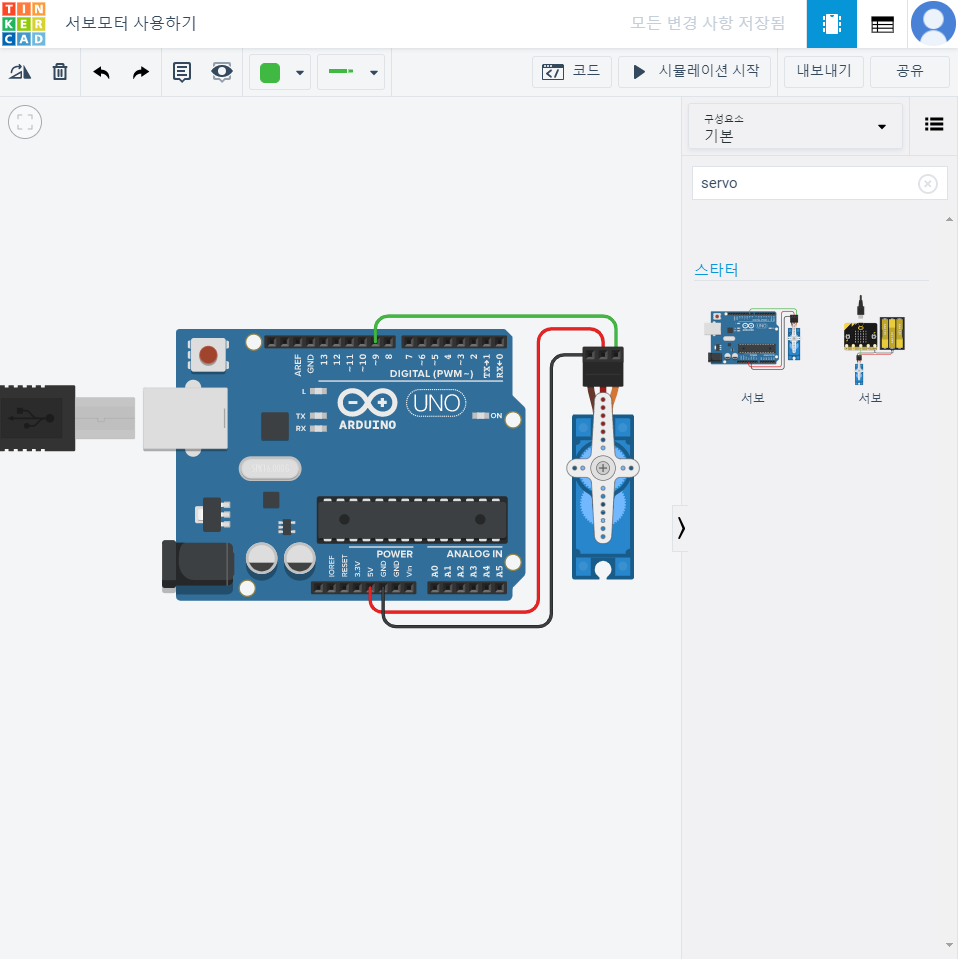
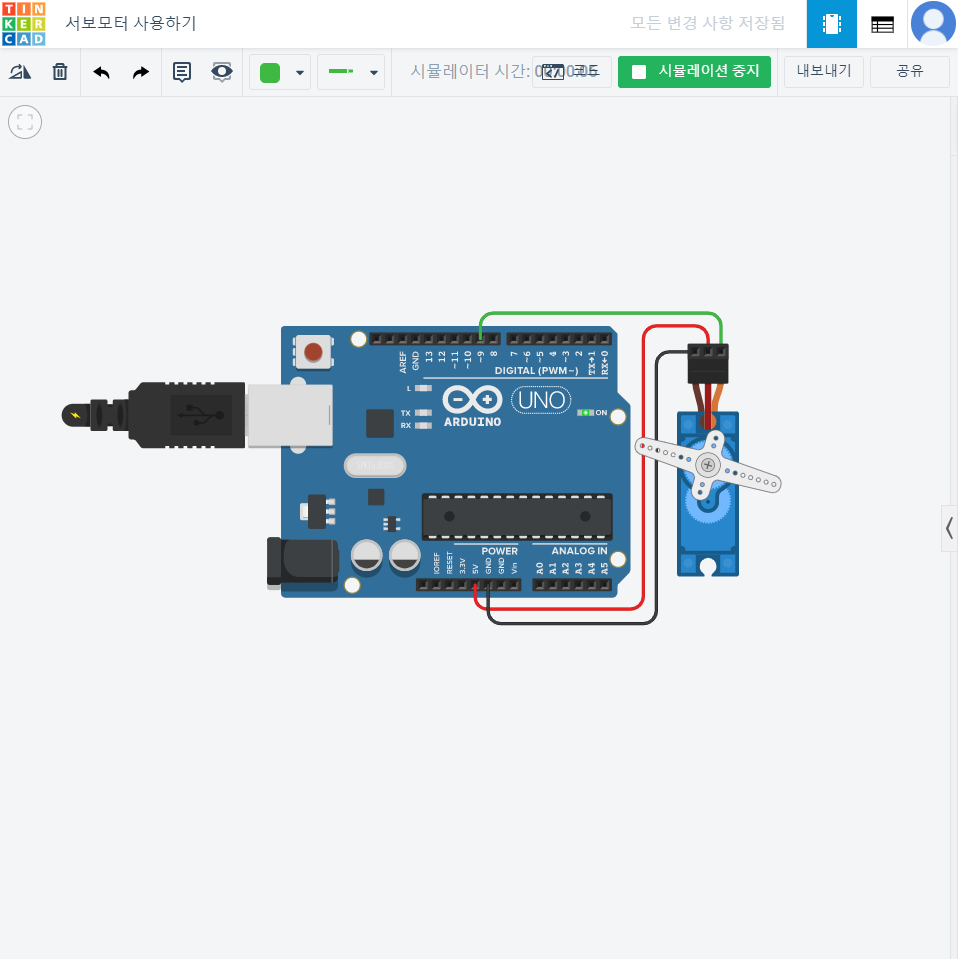
// C++ code
//
/*
Sweep
by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com>
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 Nov 2013 by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Sweep
*/
// 서보 모터 라이브러리를 불러온다.
#include <Servo.h>
int pos = 0; // 서보모터 위치변수 pos 선언
Servo servo_9;
void setup()
{
servo_9.attach(9, 500, 2500); // 9번을 서보모터에 연결하여 사용한다
}
void loop()
{
// sweep the servo from 0 to 180 degrees in steps
// of 1 degrees
for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) {
// tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
servo_9.write(pos);
// wait 15 ms for servo to reach the position
delay(15); // Wait for 15 millisecond(s)
/* pos가 180이하일때 1씩 증가 pos값으로 서보 모터의 각도조절
대기시간 0.015초*/
}
for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) {
// tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
servo_9.write(pos);
// wait 15 ms for servo to reach the position
delay(15); // Wait for 15 millisecond(s)
/* pos 가 0 이상일 때 1씩 감소ㅓ pos값으로 서보모터의 각도조절
디기시간 0.0.15초*/
}
}TMP36 아두이노 온도체크
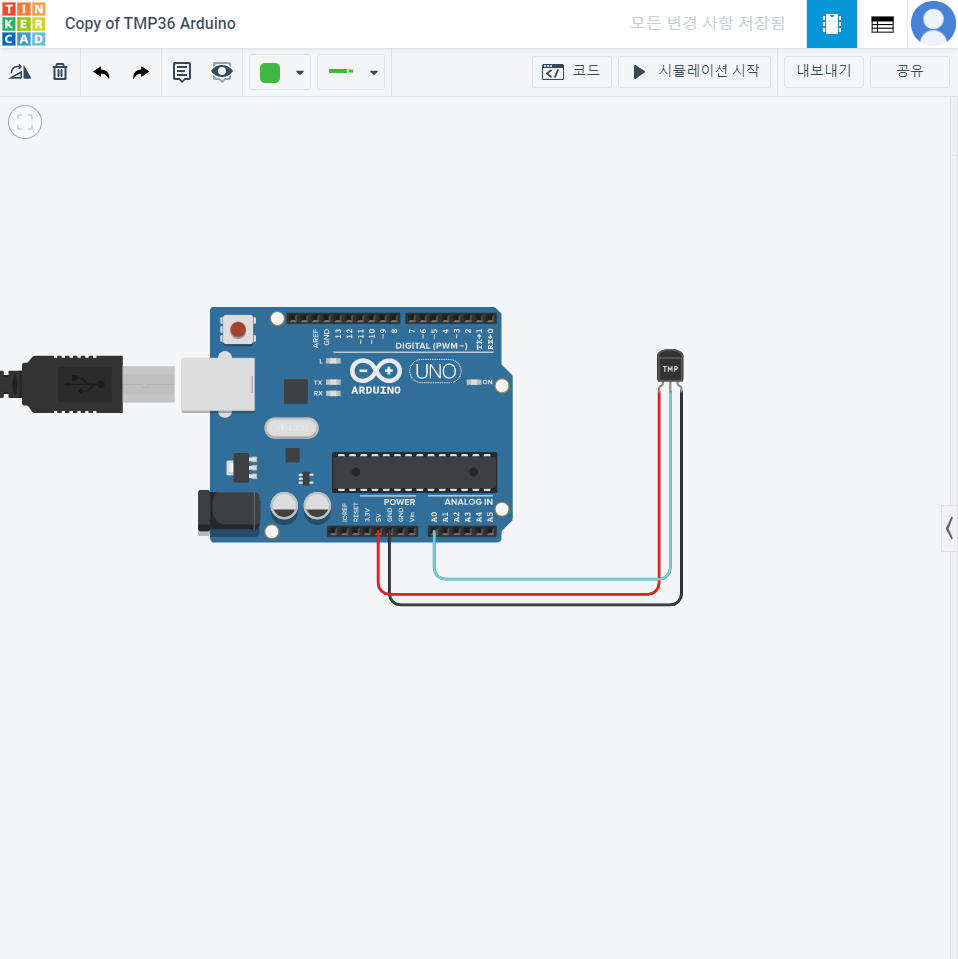
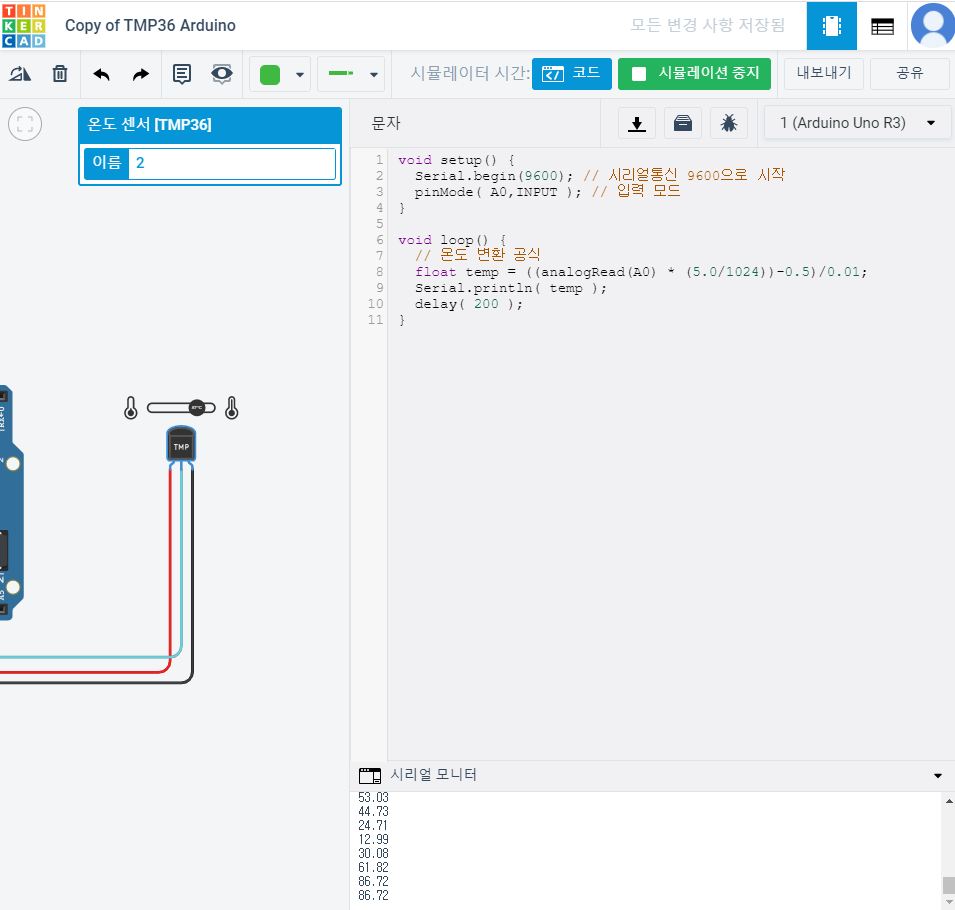
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // 시리얼통신 9600으로 시작
pinMode( A0,INPUT ); // 입력 모드
}
void loop() {
// 온도 변환 공식
float temp = ((analogRead(A0) * (5.0/1024))-0.5)/0.01;
Serial.print( temp );
Serial.println("C");
delay( 200 );
}728x90
반응형